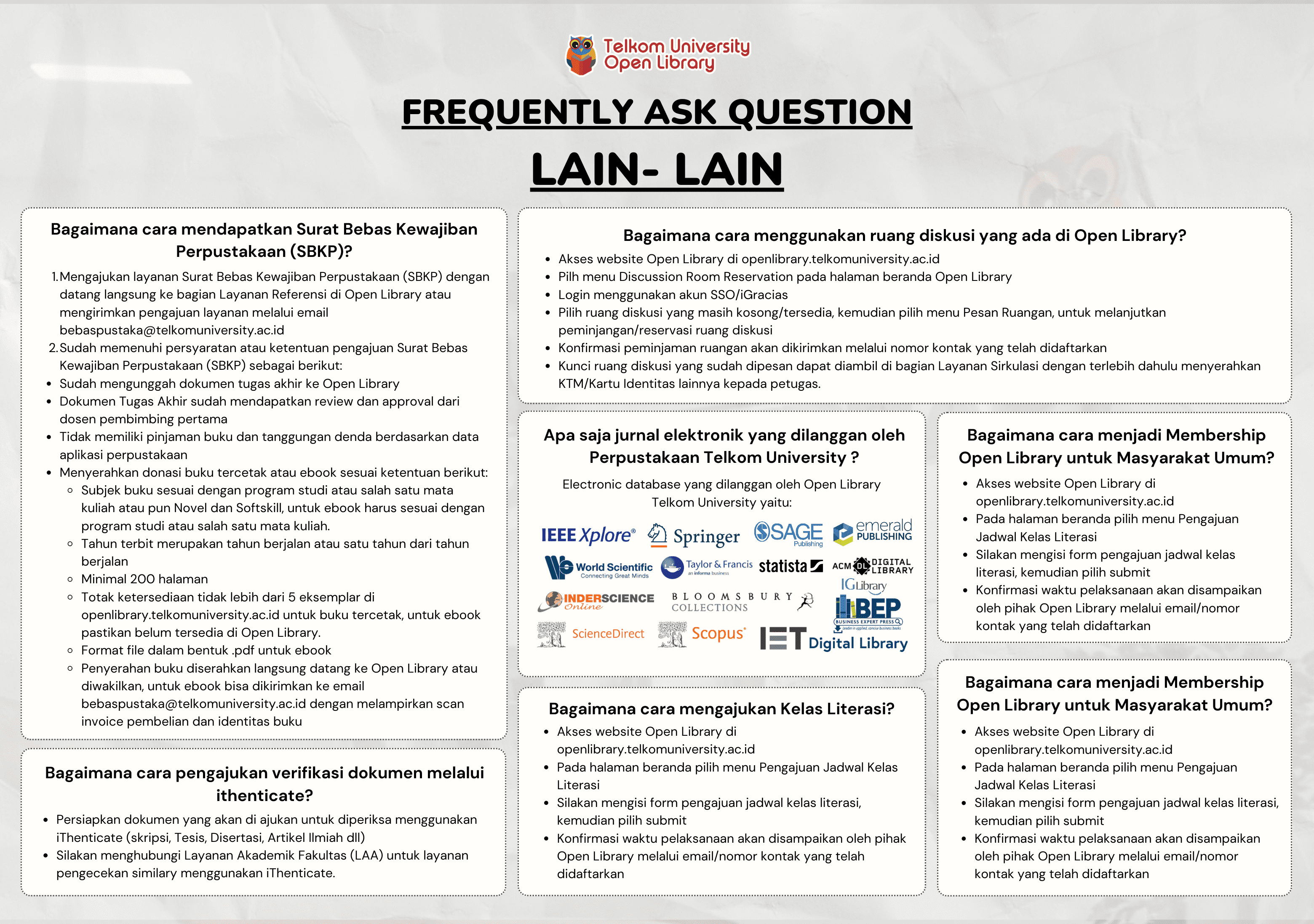
Battery Health Prediction for Electric Motorcycle using Machine Learning - Dalam bentuk buku karya ilmiah
MARSHA CLARABELL

Informasi Umum
Kode
25.05.272
Klasifikasi
000 - General Works
Jenis
Karya Ilmiah - Thesis (S2) - Reference
Subjek
Batteries Electric
Dilihat
60 kali
Informasi Lainnya
Abstraksi
Public charging stations for electric vehicles often implement battery swap<br /> systems to minimize charging times. However, these systems primarily display the<br /> State of Charge (SoC) of batteries, without providing information on the State of<br /> Health (SoH). This limitation poses a significant risk, as users may inadvertently<br /> receive degraded battery packs with an SoH of 70%–80%, increasing susceptibility<br /> to overheating and potential safety hazards, such as fires. Mitigating these risks, this<br /> study evaluates the performance of three machine learning algorithms—Random<br /> Forest (RF), Neural Network (NN), Gradient Boosting (GB), K-Nearest Neighbor<br /> (KNN), and Decision Tree (DT)—for predicting the State of Health (SoH) of bat-<br /> teries. The prediction is based on key parameters such as battery cycles, voltage,<br /> current, and State of Charge (SoC), with Depth of Discharge (DoD) derived from<br /> charging and discharging cycles serving as a critical feature for accurate estimation.<br /> Experimental results indicate that the KNN algorithm achieves the lowest Mean<br /> Absolute Error (MAE) of 2.0748%, outperforming the other methods. The slope of<br /> the battery degradation is found to be 0.02484 and the R2 score is 0.99895 which is<br /> the same as the value from the machine learning method. Consequently, the KNN<br /> method is recommended to be integrated to the public charging station. It is also<br /> successfully integrating the KNN method to the public charging system.
Koleksi & Sirkulasi
Tersedia 1 dari total 1 Koleksi
Anda harus log in untuk mengakses flippingbook
Pengarang
| Nama | MARSHA CLARABELL |
| Jenis | Perorangan |
| Penyunting | Jangkung Raharjo, Bandiyah Sri Aprillia |
| Penerjemah |
Penerbit
| Nama | Universitas Telkom, S2 Teknik Elektro |
| Kota | Bandung |
| Tahun | 2025 |
Sirkulasi
| Harga sewa | IDR 0,00 |
| Denda harian | IDR 0,00 |
| Jenis | Non-Sirkulasi |